An Overview of Juniper Networks

Juniper Networks is a leading global provider of networking solutions, aiming to revolutionize the way businesses and service providers build and manage their networks. Founded in 1996 by Pradeep Sindhu, Juniper has established itself as a key player in the networking industry, with a strong focus on high-performance, reliability, and security.
Throughout its history, Juniper Networks has consistently emphasized innovation, high-performance networking solutions, and security. The company’s routers, switches, and security products have become integral components of global networking infrastructure, serving service providers, enterprises, cloud providers, and more. With a commitment to advancing networking technology, Juniper continues to shape the future of connectivity and communication.
Juniper Networks has been at the forefront of the networking industry for decades, delivering cutting-edge solutions that empower businesses and service providers to build robust, scalable, and secure networks. With a relentless focus on innovation, Juniper has transformed the way data is transmitted, managed, and secured across the digital landscape. This in-depth article explores Juniper’s history, key products, technological contributions, and its impact on the networking ecosystem.

Product Portfolio:
Juniper Networks offers a wide range of products and solutions tailored to meet the diverse needs of modern networking environments:
Juniper Networks has a rich history that spans several decades, from its founding in the 1990s to becoming a prominent player in the networking industry. Here’s a timeline of key events in Juniper Network’s history:
1996: Juniper Networks is founded by Pradeep Sindhu with a vision to build high-performance routers capable of handling the demands of the rapidly growing internet.
1997: Juniper launches its first router, the M40, known for its innovative architecture that enables high-speed data forwarding.
1998: The M20 router is introduced, further establishing Juniper’s reputation for producing high-performance routers suitable for service providers.
1999: Juniper introduces the M160 router, which continues the company’s tradition of delivering robust and scalable routers for service provider networks.
2000: Juniper becomes publicly traded on the NASDAQ stock exchange under the symbol “JNPR,” raising substantial capital to support its growth.
2002: The T-series routers, including the T640, are launched. These routers offer even greater capacity and performance, catering to the demands of emerging high-speed networks.
2003: Juniper acquires NetScreen Technologies, expanding its portfolio to include network security solutions such as firewalls and VPN appliances.
2004: Juniper introduces the J-series routers, targeting enterprise networks and remote office connectivity.
2005: The M320 router is introduced, further enhancing Juniper’s capabilities in high-performance routing for service providers.
2006: Juniper launches the EX Series Ethernet switches, marking the company’s entry into the enterprise switching market.
2009: Juniper announces the SRX Series of services gateways, which combine routing and security functionalities in a single platform.
2010: Juniper unveils the QFX Series of switches, designed to address the needs of data center networks and cloud environments.
2012: The Junos Fusion architecture is introduced, enabling the management of thousands of devices as a single, logical entity.
2014: Juniper Networks partners with Ruckus Wireless to offer Wi-Fi solutions integrated with Juniper’s networking infrastructure.
2017: Juniper introduces the Contrail Networking platform, a software-defined networking (SDN) solution for automating and orchestrating network operations.
2018: Juniper acquires Mist Systems, a company specializing in AI-driven wireless LAN solutions, further enhancing Juniper’s wireless networking capabilities.
2020: Juniper announces its “Cloud-Ready Data Center” initiative, focusing on providing networking solutions optimized for modern cloud environments.
2021: Juniper continues to innovate in areas such as AI-driven networking, cloud-native networking, and automation, reinforcing its commitment to driving networking advancements.
Juniper Networks offers a comprehensive range of networking solutions that cater to diverse needs:
- Routing Excellence: The MX Series routers epitomize Juniper’s commitment to high-performance routing. With features like Juniper Express Path and Trio chipset, these routers offer exceptional throughput, scalability, and efficiency, making them a staple in service provider networks.
- Switching Innovation: Juniper’s EX Series switches, coupled with the Virtual Chassis technology, have redefined how data centers and campuses handle switching. The QFX Series switches extend this innovation to the world of data center fabrics, providing the high-speed, low-latency connectivity needed for modern applications.
- Security Reinvented: Juniper’s security solutions, including the SRX Series, have revolutionized network security. With advanced threat detection, intrusion prevention, and dynamic policies, Juniper’s security appliances stand as formidable guardians against cyber threats.
- Software-Defined Networking (SDN): In the era of automation and agility, Juniper’s Contrail SDN platform shines. Enabling network orchestration, automation, and analytics, Contrail empowers organizations to adapt to changing demands with ease.
Using Juniper Networks equipment involves various steps, including device setup, configuration, management, and troubleshooting. Here’s a general guide on

How to use Juniper networking devices:
1. Device Installation and Setup:
- Physical Installation: Install the Juniper device (router, switch, etc.) in a suitable rack or location with proper power and connectivity.
- Cabling: Connect power sources, network cables, and any other necessary connections according to the device’s specifications.
- Initial Power-On: Power on the device and monitor its startup process.
2. Accessing the Device:
- Console Access: Use a console cable and terminal emulation software (e.g., PuTTY) to access the device’s console port. This provides direct access to the device’s command-line interface (CLI).
- Web Interface: Some Juniper devices offer a web-based graphical user interface (GUI) for configuration and management. Access it using a web browser and the device’s IP address.
3. Configuration:
- Command-Line Interface (CLI): Use the CLI to configure the device. Log in using appropriate credentials and use commands to set up interfaces, routing protocols, security policies, and other settings.
- Configuration Hierarchy: Juniper’s CLI uses a hierarchy structure. You navigate through different levels to configure settings. Use commands like
set,edit,show, andcommitto configure and validate changes.
4. Networking Configuration:
- IP Addressing: Configure IP addresses for interfaces to enable connectivity between devices and networks.
- Routing: Set up routing protocols (e.g., OSPF, BGP) to determine how data is forwarded across the network.
- Switching: If configuring switches, set up VLANs, port configurations, and spanning tree protocols.
5. Security Configuration:
- Firewall Policies: Configure security policies to control traffic entering and leaving the network.
- Intrusion Prevention: Set up intrusion prevention and detection rules to identify and mitigate security threats.
6. Monitoring and Management:
- Show Commands: Use
showcommands to view the device’s status, interfaces, routing tables, and other configurations. - Logging: Configure logging settings to record device events and troubleshooting information.
- SNMP: Set up Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) for remote monitoring and management.
7. Software Updates:
- Junos OS Upgrades: Periodically update the Junos OS to ensure security and access new features.
- Firmware Updates: Update device firmware as needed.
8. Troubleshooting:
- Logs and Alarms: Analyze device logs and alarms to identify issues and anomalies.
- Packet Capture: Use packet capture tools to analyze network traffic.
- Troubleshooting Commands: Utilize troubleshooting commands such as
ping,traceroute, andshow interfacesto diagnose connectivity and performance issues.
Remember that Juniper’s devices and features may vary, so consult the specific device’s documentation for detailed instructions. Juniper provides comprehensive documentation and technical resources to assist users in setting up, configuring, and managing their networking equipment effectively.
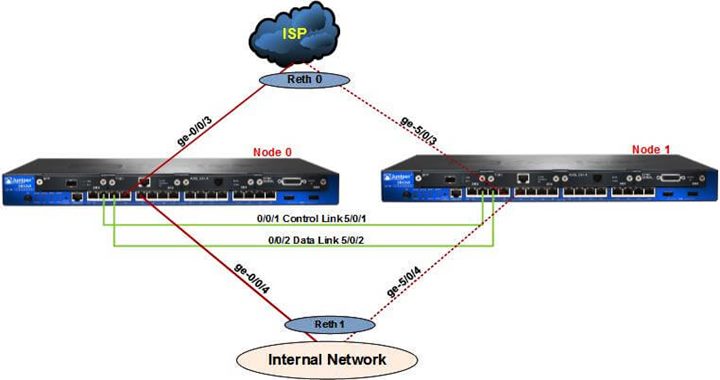
Juniper Networks SRX
Juniper Networks SRX (Services Gateway) is a series of network security and routing devices designed to provide advanced security features and routing capabilities for various network environments. The SRX series includes a range of hardware models that cater to different performance, scale, and feature requirements.
Key features of Juniper Networks SRX devices include:
- Security Services: The SRX devices offer a comprehensive suite of security services, including stateful firewall, intrusion prevention system (IPS), application visibility and control, content filtering, antivirus, antispam, and more. These services are aimed at protecting networks from various threats and attacks.
- VPN (Virtual Private Network): SRX devices support VPN technologies such as IPsec, SSL VPN, and MPLS VPN, allowing secure communication between remote sites, branches, and users over untrusted networks like the internet.
- Routing: In addition to security capabilities, SRX devices are capable routers that support various routing protocols, including BGP, OSPF, and RIP. This makes them suitable for use in network edge and branch environments where both security and routing functionalities are required.
- Unified Threat Management (UTM): SRX devices often offer UTM capabilities, combining multiple security features into a single device. This simplifies network architecture and reduces the need for multiple standalone security appliances.
- Application Visibility and Control: SRX devices can identify and control applications traversing the network, allowing administrators to enforce policies based on application usage rather than just traditional port-based rules.
- High Availability: Juniper SRX devices support high availability configurations, allowing for redundancy and failover in case of hardware or link failures.
- Junos OS: Juniper devices, including the SRX series, run on the Junos operating system. Junos provides a consistent and modular platform for configuration, monitoring, and management of network devices.
- Threat Intelligence Feeds: Juniper provides access to threat intelligence feeds that can be integrated into SRX devices to enhance their security capabilities by blocking known malicious IP addresses, domains, and URLs.
- Customization: SRX devices allow for fine-tuning and customization of security policies and rules to suit the specific needs of an organization’s network environment.
It’s important to note that Juniper’s product offerings and features may evolve over time, so it’s recommended to refer to the official Juniper Networks documentation or contact a Juniper representative for the most up-to-date and accurate information regarding the SRX series and its capabilities.

Remember that Juniper’s devices and features may vary, so consult the specific device’s documentation for detailed instructions. Juniper provides comprehensive documentation and technical resources to assist users in setting up, configuring, and managing their networking equipment effectively.
- Routing: Juniper is renowned for its cutting-edge routing platforms, including the MX Series, PTX Series, and ACX Series. These routers offer exceptional performance, scalability, and advanced features suitable for service provider and enterprise networks.
- Switching: The EX Series and QFX Series switches provide high-performance switching solutions, delivering the speed and flexibility required for modern data centers and campus networks.
- Security: Juniper’s security solutions encompass firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and secure access solutions. The SRX Series and vSRX Virtual Firewall are designed to safeguard networks from threats and ensure data privacy.
- Software-Defined Networking (SDN): Juniper’s Contrail SDN platform enables network automation, orchestration, and optimization, allowing organizations to create agile and adaptive networks.
- Cloud Solutions: Juniper assists in building cloud infrastructures that are both efficient and secure. The Juniper Networks Cloud-Enabled Branch provides connectivity and security for remote branches.
- Automation: Juniper’s Junos OS software and Juniper Extension Toolkit (JET) facilitate network automation, making it easier to manage, configure, and monitor network devices programmatically.
Key Concepts:
- Junos OS: Juniper’s network operating system, Junos OS, powers their devices and provides a consistent interface and feature set across their product portfolio.
- Juniper Mist: This is Juniper’s AI-driven wireless LAN (WLAN) solution, offering seamless connectivity, automated troubleshooting, and enhanced user experiences in wireless networks.
- Juniper OpenLab: An innovation center that promotes collaboration and exploration of emerging technologies, OpenLab fosters advancements in networking, security, and automation.
Market Presence: Juniper Networks competes with other industry giants such as Cisco Systems, Arista Networks, and Huawei in the networking space. Its solutions cater to a diverse customer base, including enterprises, telecommunications providers, cloud service providers, and government agencies.
Innovation and Impact: Juniper Networks has been instrumental in driving innovation across various networking domains. Its commitment to security, reliability, and performance has led to the development of technologies that have transformed how data is transmitted and managed.
- Software-Defined Networking (SDN): In the era of automation and agility, Juniper’s Contrail SDN platform shines. Enabling network orchestration, automation, and analytics, Contrail empowers organizations to adapt to changing demands with ease.
Technological Contributions:
- Junos OS: The heart of Juniper’s products, Junos OS, has been a driving force behind the company’s success. Its modular architecture, reliability, and feature-rich design have set industry standards for network operating systems.
- Juniper Mist: The inclusion of AI-driven solutions, such as Juniper Mist, showcases Juniper’s dedication to enhancing user experiences. Mist’s intelligent insights and automation capabilities streamline network management and troubleshooting.
- Automation Prowess: Juniper recognized early on the importance of automation. The Juniper Extension Toolkit (JET) and APIs embedded in Junos OS empower network engineers to automate configurations and operations, reducing human errors and time-to-deployment.

Impacting the Networking Ecosystem:
- Security Paradigm Shift: Juniper’s security innovations have shifted the way organizations perceive and implement network security. The concept of integrated threat intelligence, coupled with real-time protection, has become a benchmark for the industry.
- Enabling Digital Transformation: Juniper’s solutions have enabled businesses to embark on digital transformation journeys. With scalable and efficient networking components, organizations can build the agile infrastructure needed to support modern applications and services.
- Shaping Future Networks: As networks evolve, Juniper continues to be at the forefront of defining their trajectory. The company’s involvement in initiatives like cloud-native networking and its contributions to open-source projects demonstrate its commitment to shaping the networking landscape.
Key Juniper Concepts:
- Junos OS: The operating system used by Juniper devices is called Junos OS. It’s a modular, secure, and feature-rich operating system that powers Juniper routers, switches, and security devices.
- Juniper CLI: Juniper devices are configured and managed using a command-line interface (CLI). Network engineers use commands to set up and manage various aspects of the devices.
- Interfaces: Network interfaces (physical or virtual) on Juniper devices connect to other devices or networks. They can be configured with IP addresses, routing protocols, and other settings.
- Routing Protocols: Juniper devices use routing protocols to determine the best paths for data to travel across networks. Common routing protocols include OSPF, BGP, and RIP.
- Zones and Security Policies: Juniper’s security devices utilize zones and security policies to control the flow of network traffic and enforce security measures.
- Juniper Contrail: Juniper Contrail is a platform that provides software-defined networking (SDN) capabilities. It enables network automation, orchestration, and management through a centralized controller.
Remember that networking is a vast field with numerous concepts and technologies. This overview provides just a glimpse into Juniper Networks and networking basics. If you’re interested in diving deeper or have specific questions, feel free to ask.
Juniper Networks operates by providing a comprehensive range of networking solutions that enable organizations to build, manage, and secure their networks. These solutions encompass hardware, software, and services designed to deliver high performance, scalability, security, and automation. Let’s take a closer look at
How Juniper Networks works:
1. Networking Hardware: Juniper offers a variety of networking hardware devices, including routers, switches, and security appliances. These devices form the foundation of network infrastructure and are designed to handle tasks such as data forwarding, routing, switching, and security enforcement.
2. Junos Operating System (Junos OS): The Junos OS is the operating system that powers Juniper’s networking devices. It provides a consistent, modular, and feature-rich platform for configuring, managing, and operating Juniper devices. Junos OS supports a wide range of networking protocols, interfaces, and services, making it a versatile and powerful operating system for networking equipment.
3. Network Configuration: Network engineers use the Junos CLI (Command-Line Interface) to configure Juniper devices. They can set up interfaces, define routing protocols, establish security policies, and more. The Junos CLI uses a hierarchical structure, where configuration changes are made within different levels of the configuration hierarchy.
4. Routing and Switching: Juniper’s routers and switches play a crucial role in data forwarding. Routers use routing protocols to determine the best paths for data to travel between networks. Switches, on the other hand, use MAC addresses to forward data within the same network segment.
5. Security: Juniper’s security solutions are designed to protect networks from various threats. Security devices like firewalls and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) inspect incoming and outgoing traffic, enforcing security policies and filtering out malicious content.
6. Automation and Orchestration: Juniper emphasizes automation to streamline network operations. Automation tools like the Juniper Extension Toolkit (JET) and scripting languages enable network engineers to automate repetitive tasks, reducing the potential for human errors and accelerating deployment.
7. Software-Defined Networking (SDN): Juniper’s SDN solutions, such as the Contrail platform, provide centralized control and orchestration of network resources. SDN allows administrators to manage and configure networks through software, providing agility and flexibility in adapting to changing demands.
8. Cloud Integration: Juniper’s solutions are designed to integrate with cloud environments, facilitating the deployment of networks and services in cloud platforms. This integration helps organizations extend their network capabilities to the cloud while maintaining consistent management and security.
9. Analytics and Insights: Juniper devices and solutions often incorporate analytics capabilities. They can monitor network traffic, provide insights into performance, and assist in troubleshooting network issues.
10. Professional Services: Juniper offers professional services to assist organizations in designing, deploying, and optimizing their network solutions. These services can include assessments, design consultations, training, and ongoing support.
In summary, Juniper Networks works by providing a comprehensive ecosystem of networking solutions that combine hardware, software, and services to build and manage high-performance, secure, and scalable networks. These solutions enable organizations to adapt to evolving networking needs and challenges in a dynamic digital landscape.

Juniper Networks plays a significant role in the business world by providing a range of networking solutions that enable organizations to establish, manage, and secure their networks. Here’s
How Juniper Networks impacts businesses:
1. Network Infrastructure: Juniper’s networking hardware, including routers and switches, forms the backbone of modern business networks. These devices enable reliable data transmission, efficient communication, and seamless connectivity among different departments, locations, and devices.
2. Scalability and Performance: Businesses can scale their networks using Juniper’s high-performance routers and switches. Whether it’s expanding to accommodate more users, adding new branches, or increasing data capacity, Juniper’s solutions provide the necessary performance and scalability.
3. Connectivity and Collaboration: Juniper’s networking solutions facilitate communication and collaboration within organizations. Employees can connect to shared resources, applications, and data, regardless of their physical location, leading to improved productivity and teamwork.
4. Data Center Networking: For businesses with data centers, Juniper’s networking equipment optimizes data flows, enhances data processing, and supports virtualization. This is crucial for organizations that rely heavily on data-intensive applications and cloud services.
5. Cloud Integration: Many businesses are adopting cloud computing. Juniper’s solutions enable seamless integration between on-premises networks and cloud environments, ensuring secure and efficient communication between local resources and cloud services.
6. Security Solutions: In the age of cyber threats, businesses need robust security measures. Juniper’s security appliances and firewalls protect networks from unauthorized access, malware, and other cyberattacks. This ensures the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive business data.
7. Network Performance Optimization: Juniper’s solutions, including SDN platforms like Contrail, allow businesses to optimize their network performance. Automated traffic management, application prioritization, and dynamic resource allocation ensure a seamless user experience.
8. Remote Work Enablement: The COVID-19 pandemic has emphasized the importance of remote work. Juniper’s solutions enable secure remote access, allowing employees to connect to the corporate network from various locations while maintaining security standards.
9. Network Monitoring and Analytics: Juniper’s devices often include monitoring and analytics features that help businesses gain insights into network performance, traffic patterns, and potential issues. This information is invaluable for proactive troubleshooting and optimization.
10. Innovation and Digital Transformation: As businesses undergo digital transformation, Juniper’s solutions provide the infrastructure needed to adopt emerging technologies such as IoT, edge computing, and AI. These technologies enable businesses to remain competitive and innovative.
11. Customer Experience: For businesses that provide customer-facing services, Juniper’s networking solutions can enhance customer experiences. Whether through faster website loading times, improved video conferencing quality, or reliable e-commerce platforms, Juniper’s technologies contribute to a positive customer journey.
Conclusion:
In essence, Juniper Networks is integral to modern business operations, supporting connectivity, security, innovation, and efficiency. Its solutions enable businesses to adapt to technological advancements, connect with customers and partners, and navigate the complex landscape of networking and data management.
In conclusion, Juniper Networks stands as a beacon of innovation and reliability in the networking industry. From its inception, the company has strived to push the boundaries of what’s possible in networking technology. With a robust portfolio of products, a history of technological breakthroughs, and a profound impact on the networking ecosystem, Juniper Networks remains a driving force in the digital transformation era.
Juniper Networks remains a force to be reckoned with in the world of networking. Through its robust product portfolio, dedication to innovation, and emphasis on security, Juniper continues to shape the networking landscape, enabling organizations to build powerful and secure network infrastructures to meet the demands of the digital age.
Writer: Tahsin Ahmed
